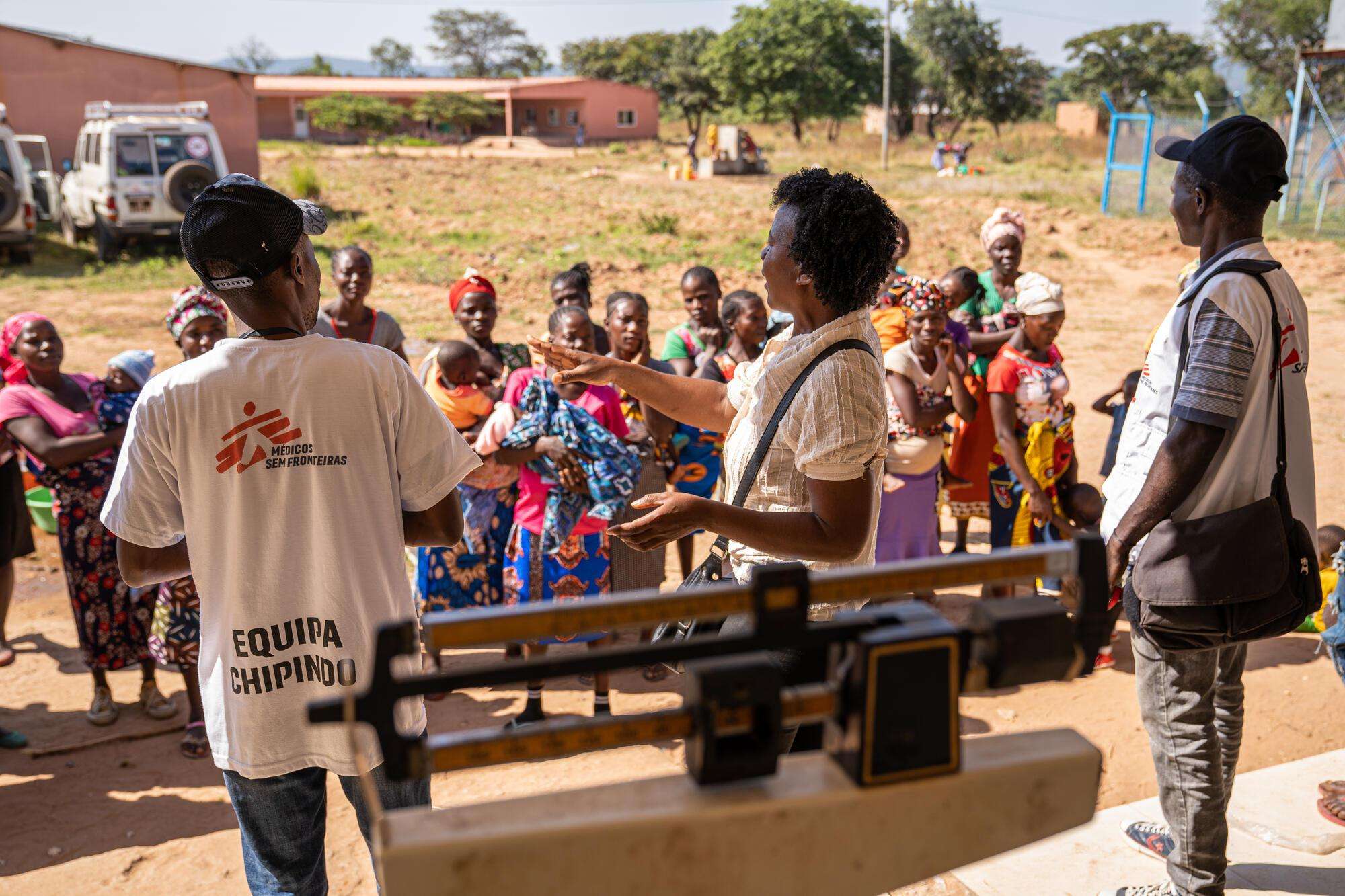
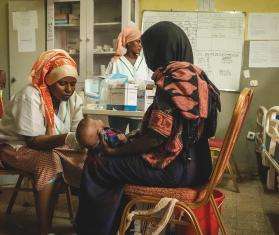
Malnutrition and malaria are common in remote communities in Angola, especially during times of drought and heavy rain. Women and their children are most affected. Access to care is critical to survival, but care is unreachable in some areas of Huíla and Benguela provinces that are located far away from medical facilities. For the past year, Doctors Without Borders/Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) has been collaborating with local health authorities to reduce the burden of these diseases in these regions.
“It’s hard to get to the health post, it takes me two hours walking,” said Domingas Luciana after a medical consultation for her daughter, Florença, at a mobile clinic run by MSF in Camassissa, a remote area of southwestern Huíla province. “[My daughter] was born very skinny and wouldn’t get better.”


From left: Domingas Luciana's daughter Florença upon finishing treatment for severe malnourishment and malaria; A child is screened for malnutrition by a community health worker in Cuvango. Angola 2023 © Mariana Abdalla/MSF
MSF teams diagnosed Florença with severe acute malnutrition and malaria—a common dual diagnosis—and enrolled her in MSF’s outpatient malnutrition program at the local hospital, as well as providing her with medication for malaria. In just three weeks, her health significantly improved. “Since I have been taking her to this mobile clinic and to the hospital for follow up [care], Florença has been getting better. I get very happy seeing that my baby has recovered,” said Domingas.
Reaching mothers and children in remote communities
Malaria is the world’s most deadly parasite, killing roughly half a million people each year. The mosquito-borne disease is prevalent in Angola: of more than 29,800 medical consultations MSF provided between February and June 2023 in Chipindo and Cuvango, Huíla province, 80 percent resulted in a malaria diagnosis. The disease is preventable, but is often fatal without treatment, especially for young children. But treatment is not easily accessible in some areas of Huíla.
“A lot of communities here live very far from a health facility,” said Isabel Severino, MSF health promotion and community engagement supervisor in Cuvango.



From left: Patients travel to health facilities using a local transport service known as kaleluias; women from Chipindo wash their hands before their children’s consultations; MSF teams build a bridge connecting remote communities to health facilities. Angola 2023 © Mariana Abdalla/MSF
To reach people without access to nearby health facilities, MSF teams are using mobile clinics and training health workers from within the community to treat mild cases of malaria and other diseases. Part of this training is learning how to identify children who need additional care at one of the 17 health facilities supported by MSF.
“Usually, women [come to] me because they’re the ones taking care of the kids,” said Joana Mandavela, a community health worker from Cuvango. “I take care of their kids like I take care of mine.”
MSF also supported a referral system using a local truck service known locally as kaleluias to transport mothers and their children to health facilities. During the time it was operating, this referral system helped 300 patients reach medical care.
Supporting children’s recovery in health facilities
Children with moderate and severe acute malnutrition were enrolled in MSF’s outpatient program, where they received ready-to-use therapeutic food, as well as kits including blankets, cups, and soap. Children in a critical state were admitted to the inpatient malnutrition unit in the hospital.
MSF treated 710 children for acute malnutrition, including two-year-old Rosa. “When Rosa was admitted at Cuvango Municipal Hospital, she had blisters all over her body,” said Isabel Zua, an MSF psychologist. “She spent a lot of time in bed and lost some of her mobility. So, after a few weeks, as she started getting better, we began to also do psycho-stimulation with her. After two sessions we could already see a big difference.”
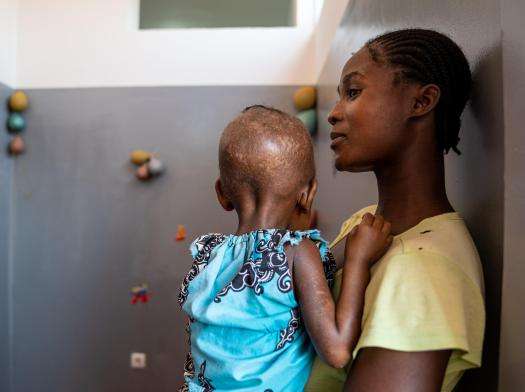
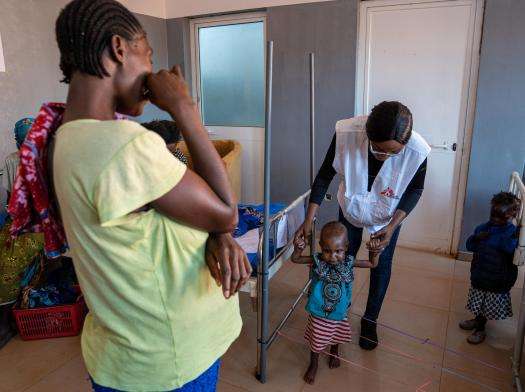
From left: Paulina Cassombu's daughter, Rosa, couldn't walk due to severe malnutrition when she was admitted to Cuvango Municipal Hospital; after three weeks of treatment, Rosa regains mobility. Angola 2023 © Mariana Abdalla/MSF
Psychologists like Isabel try to re-establish mobility, cognition, confidence, and the mother-to-child bond after a child has been in critical condition in the hospital for an extended period. “She is a lot better, and I am very happy,” said Paulina Kassombo, Rosa’s mother.
"If a child is hospitalized for a long time due to severe malnutrition, they can lose some physical and cognitive capacities," said Isabel. "When I see that the sessions I do are helping a child to walk again, for example, from the bottom of my heart, it's better than a salary."

"We are fighting to bring knowledge and empowerment to [mothers]," says Isabel Severino, MSF health promotion and community engagement supervisor.
Angola 2023 © Mariana Abdalla/MSF

Joana Mandavela is a mother of two and a community health worker in Cuvango. Both of her daughters have recovered from malnutrition.
Angola 2023 © Mariana Abdalla/MSF

"When I see patients getting results so quickly, I say to myself: it's worth being a psychologist, the work I do is magical," says Isabel Zua, an MSF psychologist.
Angola 2023 © Mariana Abdalla/MSF
Building capacity and structures for the long run
Beyond the medical work, MSF’s logistics and water and sanitation teams also rehabilitated health facilities and waste zones, and completed other construction projects, including re-building a crucial bridge connecting more than 10 remote villages to the health center in Galangue.
As part of the response in Angola, MSF conducted trainings with staff from the Ministry of Health and community health care workers, focusing on malaria, malnutrition, and managing patients in critical condition.
“The best way to prevent diseases in the long run is by leaving some knowledge and tools behind that help,” said Luis Montiel, MSF’s emergency coordinator for Huíla.
About MSF in Angola
MSF started medical activities in several locations in Angola in 2022, where years of severe drought and soaring food prices increased the risk of malaria and malnutrition. In Huíla province, MSF teams completed mobile clinics in late May and handed over its support to local health facilities to the Ministry of Health in June. As part of this handover, MSF donated supplies, motorcycles, and motorized tricycles to ensure that referral care remains accessible to patients. MSF is still present in the province of Benguela since April 2022.